A medulloblastoma is a common type of brain tumor.
What is the Pathology of Medulloblastoma?
Etiology: The cause of Medulloblastoma is not known.
Genes involved: PTCH2 on chromosome 1p32, CTNNB1 on chromosome 3p, and APC on chromosome 5q.
Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to medulloblastoma arises from remnants of the primitive neuroectoderm in the roof of the fourth ventricle.
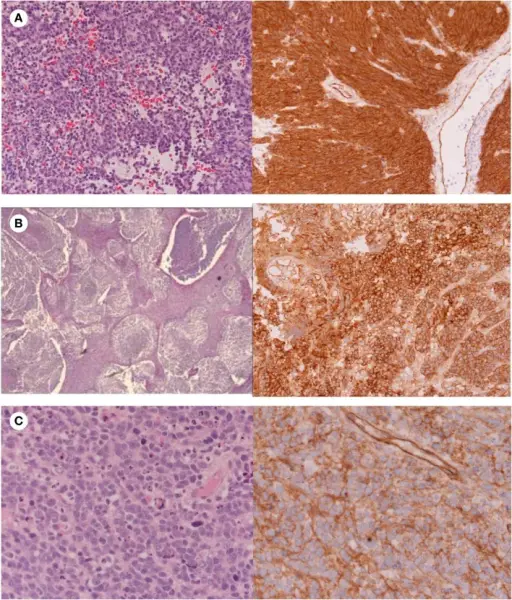
Histology: The histology associated with medulloblastoma is characterized by small cells with round to ovoid nuclei, Homer Wright rosettes, and no significant cytologic atypia or pleomorphism.
How does Medulloblastoma Present?
Patients with medulloblastoma typically are children of age four or younger. They can also be patients of age 5-14 years. Males are predominantly affected. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with Medulloblastoma include headaches, nausea, and vomiting. Medulloblastoma is associated with certain inherited diseases, which include Li-Fraumeni syndrome, and nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome (Gorlin syndrome).
How is Medulloblastoma Diagnosed?
Medulloblastoma is diagnosed by biopsy.
How is Medulloblastoma Treated?
Medulloblastoma is treated primarily by surgery.
What is the Prognosis of Medulloblastoma?
The prognosis of Medulloblastoma is poor.