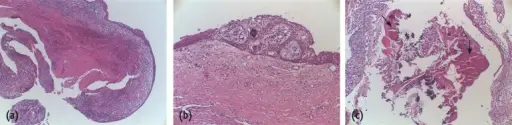
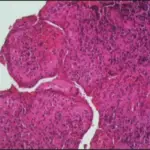
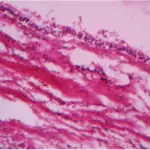
A periapical cyst is also known as radicular cysts, are the most frequent cystic lesion related to teeth and result from an infection of the tooth.
What is the Pathology of Periapical Cyst?
The pathology of periapical cyst is:
-Etiology: The cause of periapical cyst is root infection involving tooth decay.
-Genes involved: MMP2 and MMP3
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to periapical cyst epithelial cells from the rest of Malassez at the apex of the roots of a tooth become stimulated due to the body’s inflammatory response.
How does Periapical Cyst Present?
Patients with periapical cyst typically affect males present at the range of 20 to 60 years. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with periapical cyst include swelling and pain. Initially, the cyst swells to a round hard protrusion, but later on, the body resorbs some of the cyst walls, leaving a softer accumulation of fluid underneath the mucous membrane. Secondary symptoms of periapical cysts include inflammation and infection of the pulp causing dental caries. This infection is what causes necrosis of the pulp.
How is Periapical Cyst Diagnosed?
Periapical Cyst is diagnosed through oral examination and laboratory tests
How is Periapical Cyst Treated?
Periapical Cyst is treated by root canal treatment or marsupialization.
What is the Prognosis of Periapical Cyst?
The prognosis of periapical cyst is good. Complete healing was observed in 75.0% of cases.