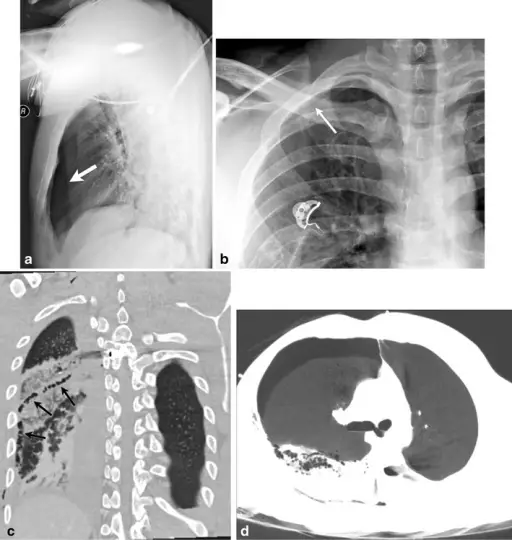
Pneumothorax is a condition characterized by the presence of air in the pleural cavity.
What is the Pathology of Pneumothorax?
The pathology of pneumothorax is:
-Etiology: The cause of pneumothorax is trauma to the chest wall cavity, certain disease progression
-Genes involved: FLCN gene mutation.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to pneumothorax is the entry of air in the pleural cavity that leads to increased pressure if the amount is too much to be reabsorbed to the lungs making it collapse. once it has collapsed the mediastinum is pulled to the unaffected area.
-Histology: The histology associated with pneumothorax shows collapsed air spaces.
How does Pneumothorax Present?
Patients with pneumothorax are typically men with a higher risk than females and although it can occur in all ages then peak age is 16-64 years and also relatively higher in the neonatal stages. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with pneumothorax include dyspnea, cyanosis, chest pain, increase heart rate, and shortness of breath.
How is Pneumothorax Diagnosed?
Pneumothorax is diagnosed by use of a chest x-ray since it clearly shows the pathology but also a CT scan can be used together with history taking and also physical exam.
How is Pneumothorax Treated?
a patient with pneumothorax is treated by preventing or managing the underlying cause of increased pleural pressure, getting rid of excess air through chest tube insertion, and later by preventing recurrence of the cause.
What is the Prognosis of Pneumothorax?
The prognosis of pneumothorax is dependent on the extent of the pressure.it has a good prognosis if the pressure is minimal and a poor prognosis if the pressure is a lot.