A primary CNS lymphoma is a rare form of extranodal non-Hodgkin lymphoma that is typically confined to the brain, eyes, and cerebrospinal fluid without evidence of systemic spread.
What is the Pathology of Primary CNS Lymphoma?
Etiology: The cause of primary CNS lymphoma is unknown. It is common in immunocompetent patients and elderly.
Genes involved: The failure of DNA double-strand breaks may lead to the formation of malignant cells.
Pathogenesis: Central nervous system is an immune privileged site and the lymphoma itself may have genetic and phenotypic features that protect the tumor from ongoing immune surveillance. Neoplastic cells may arise from lymphocytes normally residing in the immune privileged milieu of the CNS or from lymphocytes that transform to a malignant clone outside the CNS.
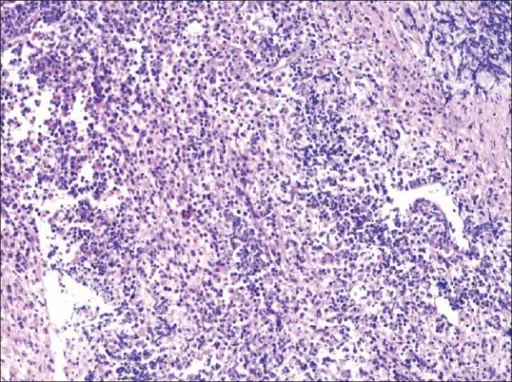
Histology: The histology associated with primary CNS lymphoma shows a vasocentric growth pattern and high lymphocyte proliferation, explaining its diffuse infiltration in the central nervous system (CNS).
How does Primary CNS Lymphoma Present?
Patients with Primary CNS lymphoma are typically males and the common age group is above 45 years of age. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with primary CNS lymphoma include nausea, vomiting, weight loss, and confusion.
How is Primary CNS Lymphoma Diagnosed?
Primary CNS lymphoma is diagnosed by biopsy.
How is Primary CNS Lymphoma Treated?
Primary CNS lymphoma is treated by high dose methotrexate.
What is the Prognosis of Primary CNS Lymphoma?
The prognosis of primary CNS lymphoma is poor.