Primary ovarian carcinoid tumors within a cystic teratoma are relatively rare tumors that resemble well-differentiated neuroendocrine tumors of the gastrointestinal tract.
What is the Pathology of Primary Ovarian Carcinoid Tumors within a Cystic Teratoma?
The pathology of primary ovarian carcinoid tumors within a cystic teratoma is:
-Etiology: The cause of primary ovarian carcinoid tumors within a cystic teratoma is unknown.
-Genes involved: CDX2.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to primary ovarian carcinoid tumors within a cystic teratoma.
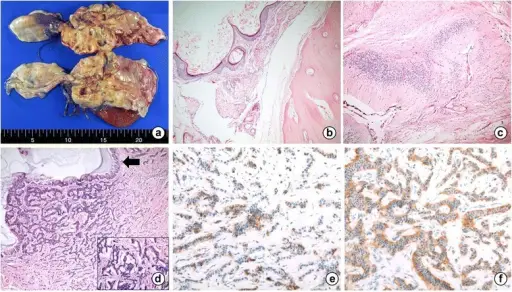
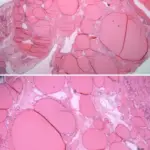
-Morphology: The morphology associated with primary ovarian carcinoid tumors within a cystic teratoma shows multicystic masses containing viscous sebaceous material and hairs.
-Histology: The histology associated with primary ovarian carcinoid tumors within a cystic teratoma shows cysts with different tissue types.
How does Primary Ovarian Carcinoid Tumors within a Cystic Teratoma Present?
Patients with primary ovarian carcinoid tumors within a cystic teratoma typically females at intra- or postmenopause or >40 years age. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with primary ovarian carcinoid tumors within a cystic teratoma include: pelvic mass, abdominal distension and pelvic pain, abnormal uterine bleeding.
How is Primary Ovarian Carcinoid Tumors within a Cystic Teratoma Diagnosed?
Primary ovarian carcinoid tumors within a cystic teratoma is diagnosed by CT scan, MRI, ultrasonography, blood tests for CA125 levels, physical examination, and biopsy.
How is Primary Ovarian Carcinoid Tumors within a Cystic Teratoma Treated?
Primary ovarian carcinoid tumors within a cystic teratoma is treated by: hysterectomy with bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy, and fertility-sparing surgery.
What is the Prognosis of Primary Ovarian Carcinoid Tumors within a Cystic Teratoma?
The prognosis of primary ovarian carcinoid tumors within a cystic teratoma is good. Generally most of the patients remain clear of tumour recurrence or metastasis during follow-up.