A ranula is a fluid collection or cyst that typically form under the tongue.
What is the Pathology of Ranula?
The pathology of ranula is:
-Etiology: The cause of ranula is disruption of flow of secretions from salivary glands.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to ranulas is when one of the salivary glands, usually the sublingual gland, is injured or diseased and the saliva no longer reaches the external surface of the mouth.
-Morphology: Oral lesion.
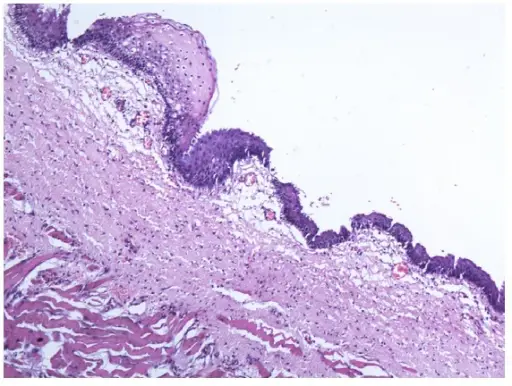
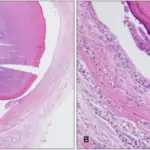
-Histology: The histology associated with ranula shows a well-delineated cavity that contains free mucinous material, the cavity wall lacking an epithelial lining.
How does Ranula Present?
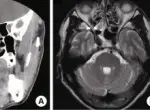
Patients with ranula are typically male or female that are typically younger. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with ranula include large, swelling, cystic, translucent to blue lesions on the floor of the mouth.
How is Ranula Diagnosed?
Ranula is diagnosed primarily by physical examination.
How is Ranula Treated?
Ranula is treated by open surgical drainage or removal.
What is the Prognosis of Ranula?
The prognosis of ranula is good.