Residual cysts are essentially radicular cysts without the presence of the offending dentition.
What is the Pathology of Residual Cyst?
-Etiology: The cause of residual cyst results from the extraction of a tooth with a radicular cyst. Trauma, carious lesion, or bacterial colonization of developmental anomaly affecting tooth irreversibly injures dental pulp.
-Genes involved: None.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to residual cyst is initiated by the spread of bacteria from a non-vital tooth in the periapical region of the jaw.
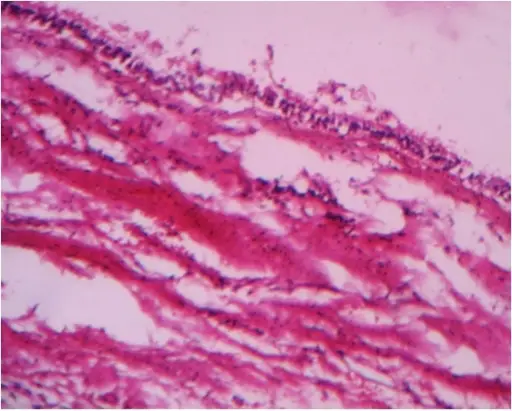
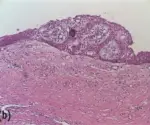
-Histology: The histology associated with residual cyst shows stratified squamous epithelium which may demonstrate exocytosis, spongiosis, or hyperplasia.
How does Residual Cyst Present?
Patients with Residual Cyst typically accounts for 10% of all jaw cysts. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with residual cyst include a range from asymptomatic and only incidentally detected on imaging, to the expansion of the affected jaw region, to pain and drainage.
How is Residual Cyst Diagnosed?
Residual Cyst is diagnosed by laboratory tests.
How is Residual Cyst Treated?
Residual Cyst is treated by excising surgically, even in the absence of symptoms.
What is the Prognosis of Residual Cyst?
The prognosis of Residual Cyst is good. Residual cysts do not recur after appropriate management.