Sebaceous adenoma is a small benign nodule that occurs mostly at the face and arises from the sebaceous gland.
What is the Pathology of Sebaceous Adenoma?
The pathology of sebaceous adenoma is the study of the abnormality of the sebaceous gland.
-Etiology: The cause of sebaceous adenoma is genetic predisposition.
-Genes involved: MLH1, MSH2, MSH6.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to sebaceous adenoma; the mismatch repair proteins, expression of PMS2, MSH2, MLH1, and MSH6, has been advocated as a first-line.
-Morphology: The morphology associated with sebaceous adenoma shows yellow papules mostly located at the head or face and can range from 0.5 – 9.0 centimeters.
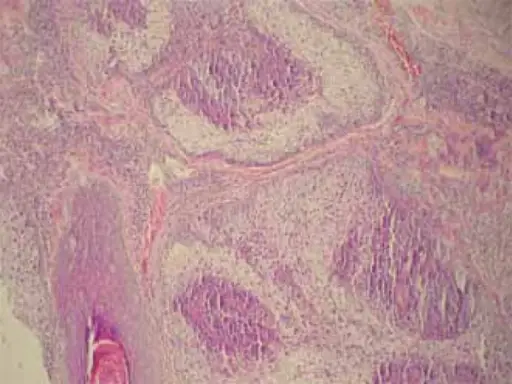
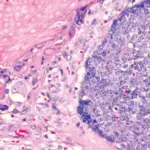
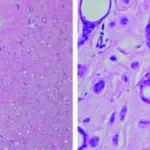
-Histology: The histology associated with sebaceous adenoma shows sebaceous glands that are incompletely differentiated and have irregular lobes.
How does Sebaceous Adenoma Present?
Patients with sebaceous adenoma typically occur equally to both men and women with a mean age of 60 years. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with sebaceous adenoma include slow-growing and are mostly asymptomatic.
How is Sebaceous Adenoma Diagnosed?
The sebaceous adenoma is diagnosed with blood work-ups, skin biopsy, CT scan, and MRI.
How is Sebaceous Adenoma Treated?
The sebaceous adenoma is treated by surgical, removal of the adenoma and long term monitoring.
What is the Prognosis of Sebaceous Adenoma?
The prognosis of sebaceous adenoma is good.