A thalasemia is a syndromes group of genetic anemias of varying clinical severity.
What is the Pathology of A Thalasemia?
The pathology of α thalasemia is:
-Etiology: The cause of α thalasemia is gene mutation.
-Genes involved: α-globin genes
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to α thalassemia are as the results from variety of molecular lesions result, but the most commonly deletion of α-globin.
-Morphology: The morphology associated with α thalasemia shows abnormal rashes.
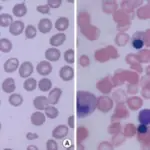
-Histology: The histology associated with α thalasemia shows abnormal red blood cells.
How does A Thalasemia Present?
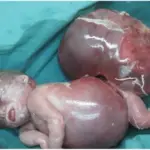
Patients with α thalasemia typically have no sex prevarence present at age range of infancy. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with α thalasemia include, anamia, severe pallor, and hydrops fetalis.
How is A Thalasemia Diagnosed?
A thalasemia is diagnosed through laboratory evaluation such as hemoglobin electrophoresis, and genetic testing.
How is A Thalasemia Treated?
A thalasemia is treated through managing symptoms if any, iron and folic acid supplementation.
What is the Prognosis of A Thalasemia?
The prognosis of α thalasemia is good for silent carriers, poor for hydrops fetalis.