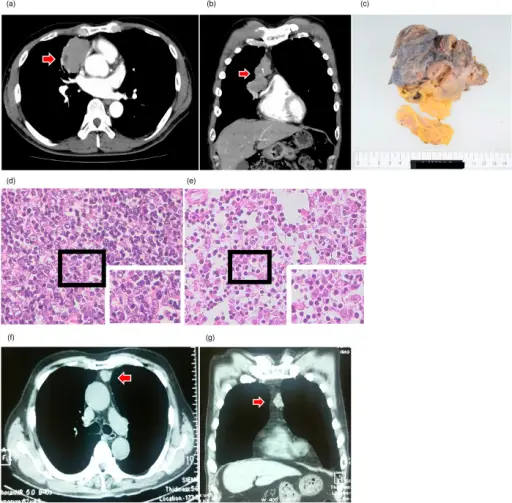
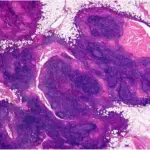
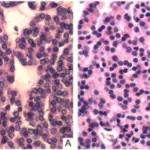
Thymomas are neoplasms of the thymus of thymic epithelial origin. Thymomas may be benign or malignant.
What are the Types of Thymomas?
The specific types of thymomas include:
- Type A
- Atypical A
- Type AB
- Type B1
- Type B2
- Type B3
- MNT
- Metaplastic Thymoma
Note that the letters in the types indicate the types of neoplastic cells that are present:
- A = Spindled
- B = Polygonal
What is the Pathology of Thymomas?
The pathology of thymomas is:
-Etiology: The cause of thymoma is unknown.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to thymoma is proliferation of thymic epithelial cells.
-Histology: Thymomas tend to have lobulated or bosselated architecture. The cellular lobules are complosed of spindled or polygonal neoplastic epithelial cells and reactive thymocytes that are intersected with fibrous bands.
How do Thymomas Present?
Patients with thymomas are typically in their fifties, and there is no sexual or racial associated risks.
How are Thymomas Diagnosed?
Thymomas are diagnosed by physical exam, imaging, and biopsy.
How is Thymoma Treated?
Thymomas are treated by surgical resection.
What is the Prognosis of Thymoma?
The prognosis of thymomas is generally good if diagnosed and treated early.