A thyroglossal duct cyst is a mass or lump in the front part of the neck that is filled with fluid.
What is the Pathology of Thyroglossal Duct Cyst?
The pathology of thyroglossal duct cyst is:
-Etiology: The cause of thyroglossal duct cyst is the abnormal development of the cells in the thyroid gland between the 4th and 8th week of fetal development.
-Genes involved: None.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to thyroglossal duct cyst involves that during embryonic development, the thyroid gland remains connected to the foramen and hyoid bone, the duct gradually disappears by the 10th week of development.
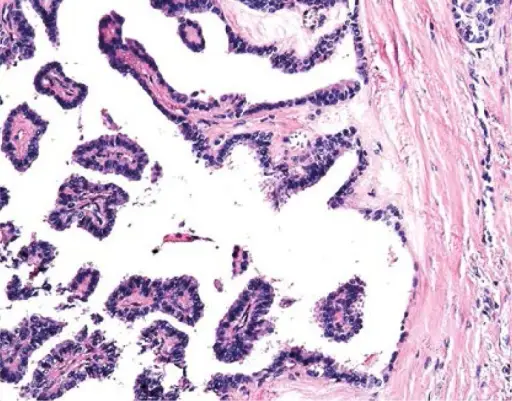
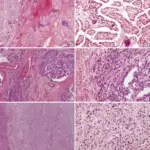
-Histology: The histology associated with thyroglossal duct cyst shows benign cells lining a cystic wall.
How does a Thyroglossal Duct Cyst Present?
Patients with thyroglossal duct cysts typically occur in both males and females. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with thyroglossal duct cyst are a subtle neck swelling without pain.
How is Thyroglossal Duct Cyst Diagnosed?
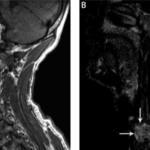
Thyroglossal duct cyst is diagnosed by physical examination and later referred to imaging.
How is Thyroglossal Duct Cyst Treated?
Thyroglossal duct cyst is treated through surgical removal.
What is the Prognosis of Thyroglossal Duct Cyst?
The prognosis of a thyroglossal duct cyst is good with excision.