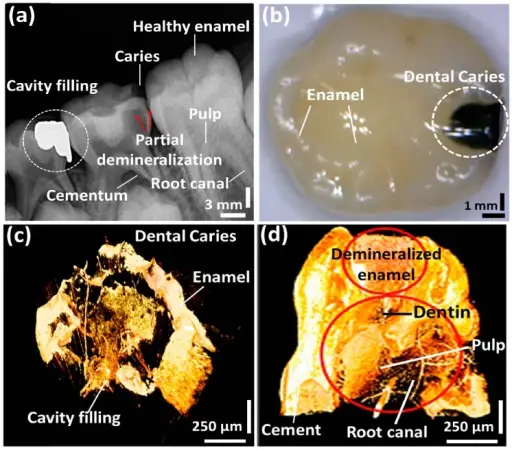
A tooth cavity is a damaged area in tooth enamel due to tooth decay. Cavities are also called dental caries or tooth decay. Cavities are caused by demineralization of tooth enamel and/or tooth dentin by acidic metabolites of fermenting sugars that are produced by bacteria in the mouth.
WHAT CAUSES CAVITIES?
Cavities are caused by many factors that include improper oral hygiene, and excessive consumption of sugar. Demineralization of enamel and dentin by acidic metabolites of fermenting sugars that are produced by bacteria in the mouth can further erode and worsen the cavity.
WHAT ARE THE SYMPTOMS OF CAVITIES?
The symptoms of cavities are broad, and depend on the severity of the cavity. Some symptoms include:
- Tooth sensitivity
- Tooth aches
- Tooth pain when eating or drinking hot or cold items
- Tooth with visible pits or holes
- Tooth with black or brown stains
WHAT ARE COMPLICATIONS OF CAVITIES?
Cavities that go untreated may become infected resulting in a tooth abscess
HOW COMMON ARE CAVITIES?
Cavities are a common problem faced by many people worldwide. Cavities are the main cause of tooth loss in people before the age of 35 years old.
HOW ARE CAVITIES DIAGNOSED?
Dentists or oral health professionals are usually capable of diagnosing and/or treating cavities. X-rays may be used to detect cavities before they are visible to the naked eye.
HOW ARE CAVITIES TREATED?
Dentists or oral health professionals are usually sought after for treating cavities. Treatment options vary depending on the severity of the cavity. Some cavity treatment options include:
- Fluoride Treatments: This promotes remineralization over the cavity.
- Acetaminophen or Ibuprofen: May be taken by some patients for pain.
- Fillings: Metallic covers often made of gold, silver, or composite resin that are used to fill the cavity.
- Root Canal: The pulp of the tooth is removed in an effort to prevent pain associated with cavities.
- Tooth Extraction: The entire tooth is removed in an effort to prevent pain associated with cavities. A dental implant may be provided to replace the tooth that was removed.
HOW ARE CAVITIES PREVENTED?
Cavities may be prevented by proper flossing, brushing, and dental cleansing on a regular and consistent basis. Good oral hygiene is critical for preventing cavities. Visit your oral healthcare professional for further information.