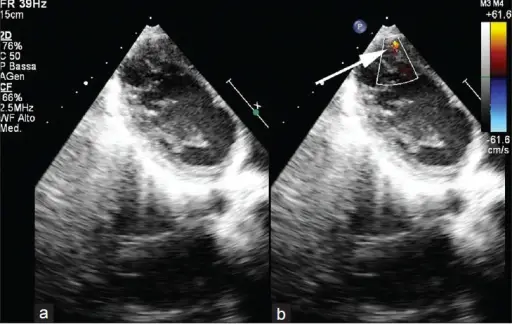
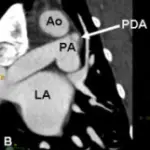
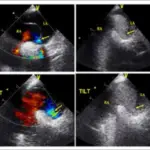
Ventricular septal defect is characterized by a hole between the right and left ventricles. Degree of symptom severity is dependent on the size of the defect: small, moderate, and large.
What is the Pathology of Ventricular Septal Defect?
Ventricular septal defect pathology is characterized by a hole in the interventricular symptom causing a left-to-right shunt.
How does Ventricular Septal Defect Present?
Ventricular septal defect can present as excessive sweating and increased sympathetic tone in infants, noted during feeding. Fatigue with feeding is usually noted. There is lack of adequate growth and frequent respiratory infections. A diastolic murmur due to aortic insufficiency is a classic finding.
How is Ventricular Septal Defect Diagnosed?
Ventricular septal defect is diagnosed with chest x-ray, MRI, and electrocardiogram. 2D echo is the imaging of choice.
How is Ventricular Septal Defect Treated?
Ventricular septal defect treatment is symptomatic, with large septal defects repaired as young as 6-12 months old. Increase in caloric intake is suggested, and medications such as diuretics, ACE inhibitors, and digoxin may be used.
What is the Prognosis of Ventricular Septal Defect?
Ventricular septal defect prognosis is good, with condition improvement after infancy, and after-repair mortality of less than 1%.