VIPoma is a neuroendocrine tumor that is characterized by in characterized by increased production of the vasoactive intestinal peptide hormone.
What is the Pathology of VIPoma?
The pathology of vipoma is:
-Etiology: The cause of VIPoma is increased production of vasoactive peptide hormone.
-Genes involved: None.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to vipoma is a result of VIP deficiency
-Morphology: None.
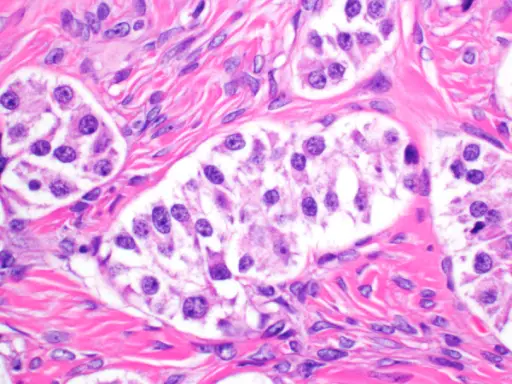
-Histology: The histology associated with VIPoma shows cells with round nuclei with low mitotic rate, and there are sheets of nests.
How does VIPoma Present?
Patients with vipoma are typically children or elderly. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with vipoma include tachycardia, muscle weakness, hepatomegaly, diarrhea and, facial flushing.
How is VIPoma Diagnosed?
VIPoma is diagnosed history taking and physical examination, radioimmunoassay, CT scan, MRI, somatostatin receptors scintigraphy.
How is VIPoma Treated?
Vipoma is treated octreotide, glucocorticoids, fluids, and electrolyte replacement therapy, systemic chemotherapy, radiotherapy, surgical exploration with tumor resection.
What is the Prognosis of VIPoma?
The prognosis of vipoma is fair since it has a survival rate of more than 5 years.