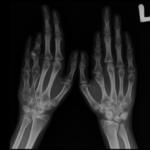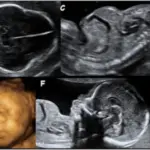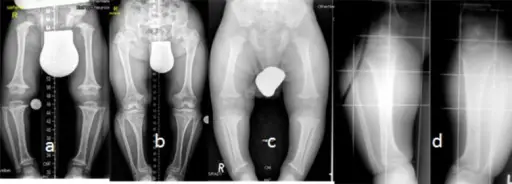
(a-d) AP radiographs of the lower limbs in achondroplasia (three boys and one girl of 6, 7, 8 and 9 years-old respectively), allmanifested the characteristic radiographic features of achondroplasia; shortness of the tubular long bones, with a relative increase in bonydiameters and densities are apparent. The metaphyses are widened and flared, but the epiphyses are uninvolved. The growth plates are U-shapedor V-shaped. This is best seen at the distal femur. The long bones, especially the tibiae, are bowed. The pelvis characteristicallyappears broad and flat, with squared iliac wings. The ilium appeared broad because the pelvis is formed almost entirely by intramemberanousossification, which is undisturbed in achondroplasia. The sciatic notches are small and the acetabuli are horizontal. Genu vara was a constantskeletal deformity encountered. In addition there was a relative shortening of the tibia compared to the fibular length. This tibial shortening istypically associated with a relevant ankle joint varus evolving during growth, the varus deformity ranged between 15 to 20°.Treatment of varus deformities of the lower limbs in patients with achondroplasia and hypochondroplasia.
Kaissi AA, Farr S, Ganger R, Hofstaetter JG, Klaushofer K, Grill F - The open orthopaedics journal (2013). Not Altered. CC.
Achondroplasia is a rare autosomal dominant genetic disorder characterized by a transmembrane mutation in the fibroblast growth factor receptor.
What is the Pathology of Achondroplasia?
The pathology of achondroplasia is:
-Etiology: The cause of achondroplasia is a point mutation.
-Genes involved: FGFR-3.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to achondroplasia is the gene coding for the transmembrane portion of FGFR3, which resides on the short arm of chromosome 4, resulting in achondroplasia.
How does Achondroplasia Present?
Patients with achondroplasia are typically males or females that are born with the condition. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with achondroplasia become more apparent in childhood, and early teenage years. Symptoms include short stature, macrocephaly, and frontal bossing.
How is Achondroplasia Diagnosed?
Achondroplasia is diagnosed by physical examination.
How is Achondroplasia Treated?
Achondroplasia is treated by supportive management and spinal decompression.
What is the Prognosis of Achondroplasia?
The prognosis of achondroplasia is generally good. Achondroplasia is the most common non-lethal skeletal dysplasia.