Acinic cell carcinoma is a malignant epithelial neoplasm involving the the salivary glands.
What is the Pathology of Acinic Cell Carcinoma?
The pathology of acinic cell carcinoma is:
-Etiology: The cause of acinic cell carcinoma is unknown.
-Genes involved: Recurrent (t[4;9][q13;q31]) genomic rearrangement.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to acinic cell carcinoma is the growth of malignant cells.
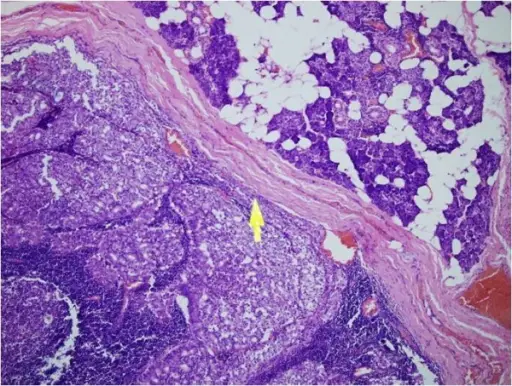
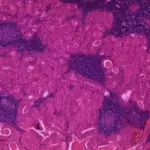
-Histology: The histology associated with acinic cell carcinoma shows microcystic, solid, papillary cystic, or follicular growth of acinar cells. The cytoplasm may be granular to vacuolated. Nuclei tend to be eccentric and round. Nucleoli tend to be conspicuous.
How does Acinic Cell Carcinoma Present?
Patients with acinic cell carcinoma typically are more common females than males, and are middle aged. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with acinic cell carcinoma include a slow growing painful mass.
How is Acinic Cell Carcinoma Diagnosed?
Acinic cell carcinoma is diagnosed by physical exam, imaging, and biopsy.
How is Acinic Cell Carcinoma Treated?
Acinic cell carcinoma is treated by complete surgical excision.
What is the Prognosis of Acinic Cell Carcinoma?
The prognosis of acinic cell carcinoma is fair to poor.