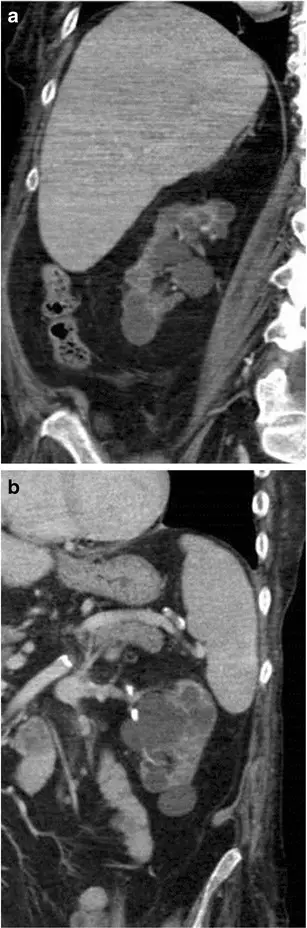
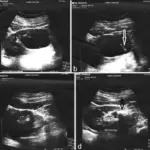
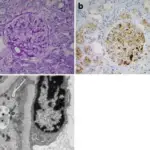
Acquired (dialysis-associated) cystic disease is numerous cortical and medullary cysts associated with prolonged dialysis due to end stage renal failure.
What is the Pathology of Acquired (Dialysis-Associated) Cystic Disease?
The pathology of acquired (dialysis-associated) cystic disease is:
-Etiology: The cause of acquired (dialysis-associated) cystic disease is dialysis-associated.
-Genes involved: None.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to acquired (dialysis-associated) cystic disease form as a result of impediment of tubules by interstitial fibrosis or by oxalate crystals.
-Morphology: The morphology associated with acquired (dialysis-associated) cystic disease shows cysts measuring 0.5 to 2 cm in diameter, containing clear fluid.
-Histology: The histology associated with acquired (dialysis-associated) cystic disease shows cysts lined with either hyperplastic or flattened tubular epithelium.
How does Acquired (Dialysis-Associated) Cystic Disease Present?
Patients with acquired (dialysis-associated) cystic disease typically have no gender preference present at the age range of adulthood. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with acquired (dialysis-associated) cystic disease include asymptomatic, hematuria.
How is Acquired (Dialysis-Associated) Cystic Disease Diagnosed?
Acquired (dialysis-associated) cystic disease is diagnosed by a medical history, Imaging tests- ultrasound, CT scan, MRI.
How is Acquired (Dialysis-Associated) Cystic Disease Treated?
Acquired (dialysis-associated) cystic disease is treated by symptomatic management, antibacterial. Surgical interventions- drainage, tumor removal and kidney transplant.
What is the Prognosis of Acquired (Dialysis-Associated) Cystic Disease?
The prognosis of acquired (dialysis-associated) cystic disease is good. The condition does not cause many complications.