Acute bacterial prostatitis is the sudden onset of inflammation of the prostate secondary to bacteria that cause urinary tract infections.
What is the Pathology of Acute Bacterial Prostatitis?
The pathology of acute bacterial prostatitis is:
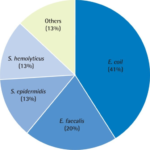
-Etiology: The cause of acute bacterial prostatitis is the infection with gram-negative members Enterobacteriaceae.
-Genes involved: Unknown.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to acute bacterial prostatitis organism reaching the prostate via lymphohematogenous routes, or infected urine flows into the prostatic and ejaculatory ducts, the organisms implants themselves in the prostate, attracts macrophages initiating inflammatory process.
-Morphology: The morphology associated with acute bacterial prostatitis shows swollen tense, and enlarged prostate. numerous abscesses and foci of necrosis on cut section.
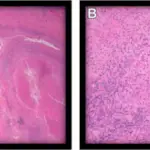
-Histology: The histology associated with acute bacterial prostatitis shows diffuse acute inflammatory infiltrate, prostatic acini filled with neutrophilic exudate.
How does Acute Bacterial Prostatitis Present?
Patients with acute bacterial prostatitis are typically older males. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with acute bacterial prostatitis include fever, chills, malaise, dysuria, perineal pain, urinary frequency, perineal tenderness, and urinary retention.
How is Acute Bacterial Prostatitis Diagnosed?
Acute bacterial prostatitis is diagnosed in laboratory studies which include urinalysis that shows leukocytes, positive urine culture, increased erum prostate-specific antigen levels (PSA). A biopsy may be obtained.
How is Acute Bacterial Prostatitis Treated?
Acute bacterial prostatitis is treated through medical care that includes antibiotic therapy. Surgical intervention for perineal aspiration of abscess may be indicated.
What is the Prognosis of Acute Bacterial Prostatitis?
The prognosis of acute bacterial prostatitis is good if treated early.