Acute interstitial pneumonia is a rare and fulminant form of idiopathic interstitial widespread acute lung injury associated with sudden onset of dyspnea and rapid pulmonary decline.
What is the Pathology of Acute Interstitial Pneumonia?
The pathology of acute interstitial pneumonia is:
-Etiology: The cause of acute interstitial pneumonia is unknown
-Genes involved: None.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to is acute interstitial pneumonia alveolar damage.
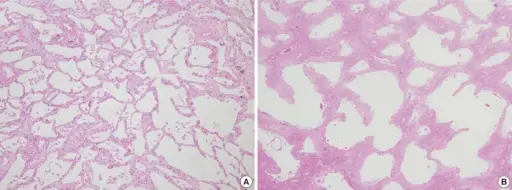
-Histology: The histology associated with acute interstitial pneumonia shows diffuse alveolar injury, diffuse interstitial fibrosis thicken spindle cell proliferation.
How does Acute Interstitial Pneumonia Present?
Patients with acute interstitial pneumonia typically have no gender preference, present at age range of the mean of 54years. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with acute interstitial pneumonia include acute hypoxemia and dyspnea, clinically ill, tachycardia, agitation, anxiety, tachypnea,on lung examination, cyanosis, peripheral vasoconstriction, and hypotension.
How is Acute Interstitial Pneumonia Diagnosed?
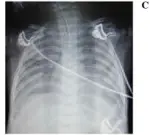
Acute interstitial pneumonia is diagnosed through Imaging studies, radiography indicates bilateral rales, CT scans, echocardiograph with features overlapping those of acute respiratory distress syndrome.
How is Acute Interstitial Pneumonia Treated?
Acute interstitial pneumonia is treated through mechanical and ventilator support.
What is the Prognosis of Acute Interstitial Pneumonia?
The prognosis of acute interstitial pneumonia is poor with a mortality rate of about 50%, most deaths happening within 1 to 2 months of the disease.