Acute lung injury is an ailment of acute inflammation causing interruption of the lung endothelial and epithelial barriers.
What is the Pathology of Acute Lung Injury?
The pathology of acute lung injury is:
-Etiology: The cause of acute lung injury is acute lung injury.
-Genes involved: None.
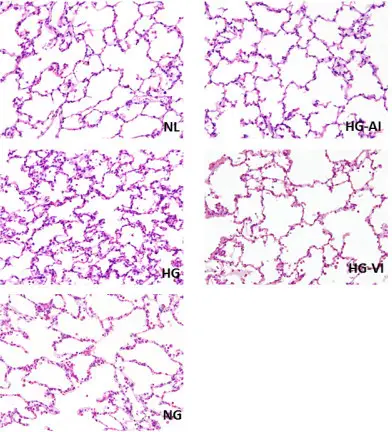
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to acute lung injury is unclear, although both local and systemic inflammatory responses occur. accumulate neutrophils are considered to play a role in the pathogenesis. Activated neutrophils release proteolytic enzymes, toxic oxygen species, and phospholipid products that upsurge the inflammatory response and cause more damage to the capillary alveolar epithelium and endothelium.
-Histology: The histology associated with acute lung injury shows injury of alveolar-capillary membrane integrity, extreme transepithelial neutrophil relocation, and pro-inflammatory, cytotoxic mediators release.
How does Acute Lung Injury Present?
Patients with acute lung injury typically have no gender prevalence present at age range of any age. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with acute lung injury include respiratory distress, an increase in respiratory rate, and signs of respiratory failure, and hypoxemia.
How is Acute Lung Injury Diagnosed?
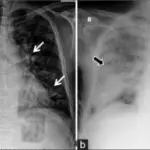
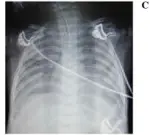
Acute lung injury is diagnosed through laboratory tests, with PaO2 less than 300, alkalosis in ABGs test. Imaging studies, Radiography, CT scans, and echocardiography.
How is Acute Lung Injury Treated?
Acute lung injury is treated through mechanical and ventilatory support.
What is the Prognosis of Acute Lung Injury?
The prognosis of acute lung injury is fair.