Acute mastitis is the infection or inflammation of breast tissue, usually bacterial, often seen in association with lactation. If inflammatory disorders are left untreated it may form abscess and fistulous tracts.
What is the Pathology of Acute Mastitis?
The pathology of acute mastitis is:
-Etiology: The cause of acute mastitis is associated with lactation, cracks in nipple, eczema, nipple dermatoses, and postreduction mammoplasty. Infections are usually due to Staphylococcus aureus. Nonpregnancy related infections may be polymicrobial or associated with diabetes.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to acute mastitis is the accumulation of inadequately drained milk in ducts and lobules that creates a microenvironment that fosters bacterial growth.
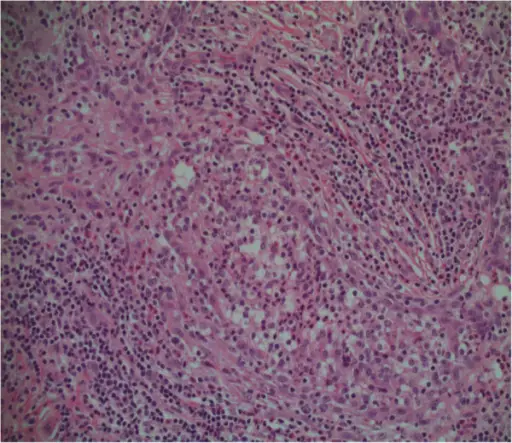
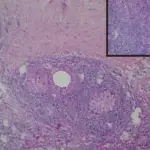
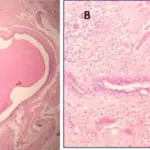
-Morphology: The morphology associated with acute mastitis shows a hypoechoic lesion on ultrasound with purulent material, well circumscribed, macrolobulated, irregular, or ill-defined with septa and thick echogenic rim. Staphylococcus aureus is the most common organism and the microscopic examination reveals a mixed dense acute inflammatory infiltrate.
-Histology: The histology associated with acute mastitis shows that it may obscure underlying normal breast tissue and the tissue necrosis may be present. Gram stain for microorganisms can reveal bacterial forms (gram positive cocci) associated with neutrophilic infiltrate, granulation tissue, and chronic inflammation with resolution.
How does Acute Mastitis Present?
Patients with acute mastitis typically are female that present at an age range of reproductive age groups. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with acute mastitis include erythema, swelling, firmness, breast pain, fever, malaise, decreased milk outflow and, an abscess.
How is Acute Mastitis Diagnosed?
Acute mastitis is diagnosed based on physical exam. Ultrasound is preferred imagining modality. The biopsy may be warranted for suspected abscess, atypical presentation, recurrent infection.
How is Acute Mastitis Treated?
Acute mastitis may be treated by incision and drainage. Analgesia, warm compress, and targeted antibiotics may be utilized as well.
What is the Prognosis of Acute Mastitis?
The prognosis of acute mastitis is good. The recurrent breast abscesses are more likely to be smokers and have mixed bacterial and anaerobic infections.