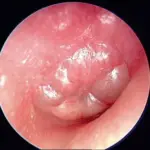
Acute otitis media is an infectious disease of the middle ear. Acute otitis media is usually a complication of eustachian tube dysfunction that occurs during a viral upper respiratory tract infection.
What is the Pathology of Acute Otitis Media?
The pathology of acute otitis media is:
-Etiology: The cause of acute otitis media is most commonly Streptococcus pneumoniae. Acute otitis media may also be caused by Haemophilus influenzae, and Moraxella catarrhalis. Acute otitis media may also be caused by fungi or Pneumocystis in immunocompromised individuals.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to acute otitis media involve a complication of eustachian tube during an acute viral upper respiratory tract infection.
-Morphology: The morphology of acute otitis media include hyperemic, opaque, and bulging tympanic membrane with limited mobility. Acute otitis media may cause purulent otorrhea and small fragments of soft or rubbery granulation tissue.
-Histology: The histology associated with acute otitis media shows acute inflammatory cells, haphazard glandular metaplasia with cilia, and hemorrhage. Cholesterol granulomas, and reactive bone formation may also be observed.
How does Acute Otitis Media Present?
Patients with acute otitis media typically are either male or female children. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with acute otitis media include earache, irritability, fussiness, fever, drainage from the ear that is thick, yellow, or bloody, loss of appetite, and vomiting.
How is Acute Otitis Media Diagnosed?
Acute otitis media is diagnosed by physical examination of the ear to check for bulging of the tympanic membrane, new onset of otorrhea or erythema.
How is Acute Otitis Media Treated?
Acute otitis media is treated with antibiotics which typically include amoxicillin, or combination of amoxicillin and clavulanate.
What is the Prognosis of Acute Otitis Media?
The prognosis of acute otitis media is good. However, there are rare complications which include mastoiditis, labyrinthitis, meningitis, or abscess.