Acute proliferative glomerulonephritis is a disease of the glomeruli that is caused by bacterial infection.
What is the Pathology of Acute Proliferative Glomerulonephritis?
The pathology of acute proliferative glomerulonephritis is the scientific study of the disease of the glomeruli caused by bacterial infection, especially the streptococcus type.
-Etiology: The cause of acute proliferative glomerulonephritis is streptococcus bacteria.
-Genes involved: Unknown.
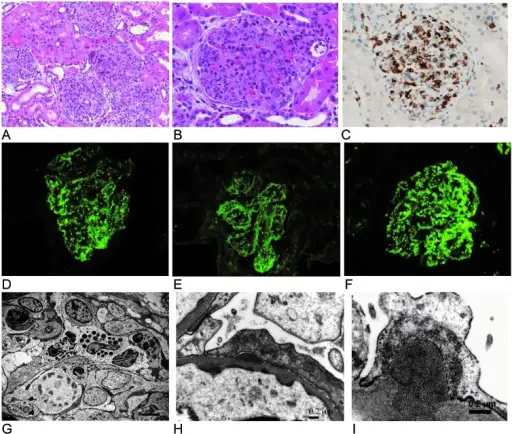
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to acute proliferative glomerulonephritis, the infection affects the blood vessels leading to inflammation of the glomeruli rendering the renal organ ineffective if the process of urine filtering.
-Morphology: Not applicable.
-Histology: The histology associated with acute proliferative glomerulonephritis shows diffuse, focal and mesangial patterns.
How does Acute Proliferative Glomerulonephritis Present?
Patients with acute proliferative glomerulonephritis typically are males present at the the age range of 5-15 years. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with acute proliferative glomerulonephritis include hematuria, oliguria, edema, hypertension, fever, headache.
How is Acute Proliferative Glomerulonephritis Diagnosed?
Acute proliferative glomerulonephritis is diagnosed with kidney biopsy, blood tests, physical examination.
How is Acute Proliferative Glomerulonephritis Treated?
Acute proliferative glomerulonephritis is treated by blood pressure control, low sodium diet, loop diuretics, beta blockers.
What is the Prognosis of Acute Proliferative Glomerulonephritis?
The prognosis of acute proliferative glomerulonephritis is good since once the symptoms are managed the disease resolves.