Acute respiratory distress syndrome is a clinical syndrome characterized by one week of respiratory distress, bilateral opacities, edema, and PaO2/FiO2 ratio <200, caused by progressive respiratory insufficiency due to diffuse alveolar damage.
What is the Pathology of Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome?
The pathology of acute respiratory distress syndrome is:
-Etiology: The cause of acute respiratory distress syndrome is direct lung injuries, burns, bacteremia, massive transfusion, sepsis, pneumonia, fractures, aspiration near-drowning fat embolism.
-Genes involved: FAS gene.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to acute respiratory distress syndrome are diffuse damage to the alveolar-capillary walls, followed by a relatively nonspecific, often predictable series of morphologic and physiologic alterations leading to respiratory failure.
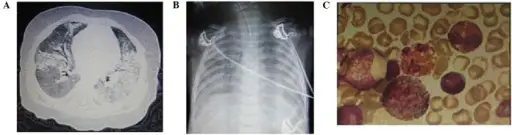
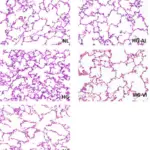
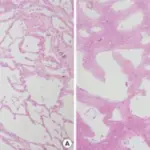
-Histology: The histology associated with acute respiratory distress syndrome shows diffuse alveolar injury, thickened alveolar walls, and the presence of hyaline membranes.
How does Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome Present?
Patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome typically have no gender prevalence present at any age range. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with acute respiratory distress syndrome include acute hypoxemia and dyspnea, clinically ill, tachycardia, agitation, anxiety, tachypnea, low PaO2/FiO2 ratio, bilateral rales on lung examination, cyanosis, peripheral vasoconstriction, and hypotension.
How is Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome Diagnosed?
Acute respiratory distress syndrome is diagnosed through laboratory tests, ABGs. Imaging studies, Radiography indicate bilateral rales, CT scans, and echocardiograph.
How is Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome Treated?
Acute respiratory distress syndrome is treated through mechanical and ventilatory support.
What is the Prognosis of Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome?
The prognosis of acute respiratory distress syndrome is poor associated with a high mortality rate due to its complications.