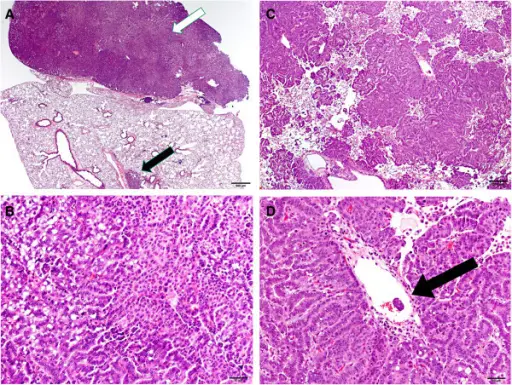
Pulmonary bronchiolo-alveolar adenocarcinomas in MCA + MWCNT treated mice. A. The photomicrograph shows a right cardiac lung lobe of a MCA + MWCNT-treated mouse that contains a bronchiolo-alveolar adenocarcinoma (white arrow). A bronchiolo-alveolar adenoma (black arrow) is in the adjacent lung lobe. (2x). The magnification bar is 500 microns. B. The figure is a photomicrograph of a bronchiolo-alveolar adenocarcinoma in the right cardiac lobe of a mouse lung treated with MCA + MWCNT (20x). This infiltrative adenocarcinoma filled ~85% of the lobe on histologic cross section. The scale bar is 200 microns. C. The photomicrograph is a higher magnification of the bronchiolo-alveolar adenocarcinoma of the right cardiac lobe in figure B showing heterogeneous growth and pleomorphic cytologic features (40x). The scale bar is 50 microns. D. The photomicrograph shows a metastasis of the bronchiolo-alveolar adenocarcinoma in the right cardiac lobe of a mouse lung 17 months following treatment with MCA + MWCNT (40×). The arrow demonstrates a metastasis in a pulmonary vein. The scale bar is 50 microns. Promotion of lung adenocarcinoma following inhalation exposure to multi-walled carbon nanotubes. Sargent LM, Porter DW, Staska LM, Hubbs AF, Lowry DT, Battelli L, Siegrist KJ, Kashon ML, Mercer RR, Bauer AK, Chen BT, Salisbury JL, Frazer D, McKinney W, Andrew M, Tsuruoka S, Endo M, Fluharty KL, Castranova V, Reynolds SH - Particle and fibre toxicology (2014). Not Altered. CC.
Adenocarcinoma is a type of cancer that starts in mucus-producing glandular cells. Many organs have these types of cells and adenocarcinoma can develop in any of these organs.
What is the Pathology of Adenocarcinoma?
The pathology of adenocarcinoma is:
-Etiology: The cause of adenocarcinoma is smoking, toxin exposure, previous radiation therapy.
-Genes involved: p53 or TP53.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to adenocarcinoma are glandular cells which secrete mucous, digestive juices or other liquids and begin to grow in the glands that line your organs, they can eventually spread to other parts of your body. This may include the brain, liver, lungs, lymph nodes, or bone.
-Histology: The histology associated with adenocarcinoma shows malignant glands.
How does Adenocarcinoma Present?
Patients with adenocarcinoma are middle aged. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with adenocarcinoma include abdominal pain, nausea, and vomiting.
How is Adenocarcinoma Diagnosed?
Adenocarcinoma is diagnosed by blood tests, CT scan, MRI, and biopsy.
How is Adenocarcinoma Treated?
Adenocarcinoma is treated by surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation therapy.
What is the Prognosis of Adenocarcinoma?
The prognosis of adenocarcinoma is poor.