Adenocarcinoma is cancer that does not fit an exact classification and it can occur in the major salivary glands (usually the parotid glands) or in the minor salivary glands. A painless lump is the most common symptom. It appears in parotid gland, submandibular gland, palate or buccal mucosa.
What is the Pathology of Adenocarcinoma of the Salivary Gland?
The pathology of adenocarcinoma is:
-Etiology: The cause of adenocarcinoma may be smoking, or toxin related.
-Genes involved: EGFR gene amplification, high HER2 gene copy number, KRAS mutation
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to adenocarcinoma is the classic malignant transformation.
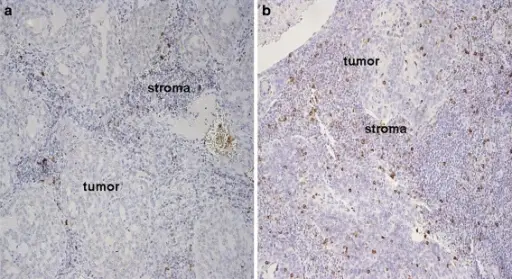
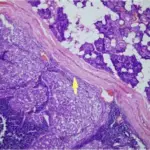
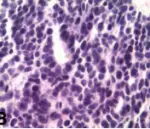
-Histology: The histology associated with adenocarcinoma glandular or ductal features involved by malignant cells.
How does Adenocarcinoma of the Salivary Gland Present?
Patients with adenocarcinoma of the salivary glands are typically males, of a wide age range. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with adenocarcinoma include a painless mass.
How is Adenocarcinoma of the Salivary Gland Diagnosed?
Adenocarcinoma is diagnosed by physical exam, laboratory testing, fine needle aspiration, and biopsy.
How is Adenocarcinoma of the Salivary Gland Treated?
Adenocarcinoma is treated by complete surgical excision.
What is the Prognosis of Adenocarcinoma of the Salivary Gland?
The prognosis of adenocarcinoma is poor. The 5 year survival rate is 60%.