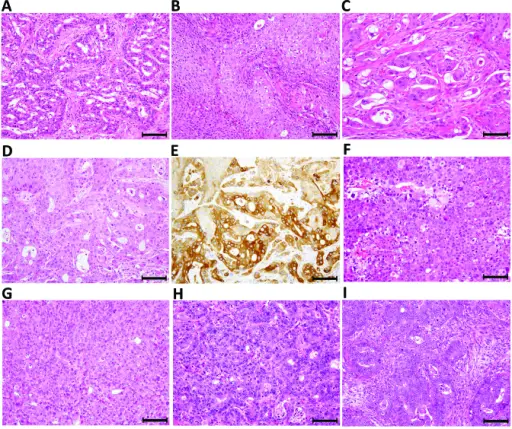
Adenosquamous carcinoma of the lung is a combination of both squamous cell carcinoma and adenocarcinoma of the lungs and falls under the category of non-small cell carcinoma.
What is the Pathology of Adenosquamous Carcinoma of the Lung?
The pathology of adenosquamous carcinoma is:
-Etiology: The cause of adenosquamous carcinoma is smoke from an either cigarette, car exhaust fumes asbestos and silica, and air pollution.
-Genes involved: EGFR and KRAS.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to adenosquamous carcinoma of the lungs is, carcinogenic binding to cell’s DNA and damage the cell, abnormal cell growth occur malignant pulmonary epithelial transformation, abnormal proliferation of the lung cells, to non-specific inflammatory changes leading to lesion formation.
-Histology: The histology associated with adenosquamous shows glandular elements to papillary lesions, also shows bronchioloalveolar growth pattern.
How does Adenosquamous Carcinoma of the Lung Present?
Patients with adenosquamous carcinoma typically have been marked increases female, linked to smoking, present at age mean range of 71 years. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with adenosquamous include asymptomatic having nodules, hemoptysis, cough, or inadvertent weight loss.
How is Adenosquamous Carcinoma of the Lung Diagnosed?
The adenosquamous carcinoma is diagnosed specifically using the pathology presentation. However, other means of diagnosis are lung biopsy and also chest x-ray.
How is Adenosquamous Carcinoma of the Lung Treated?
In treatment, adenocarcinoma is treated mostly using surgical resection of the affected lung or lobe (lobectomy) and lymph nodes (lymphadenectomy). Others are chemotherapy and radiotherapy.
What is the Prognosis of Adenosquamous Carcinoma of the Lung?
The prognosis of adenosquamous carcinoma is poor.