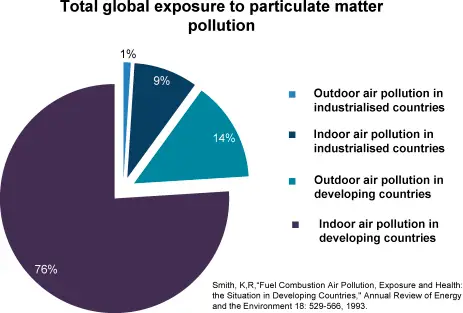
Air pollution is the contamination of the indoor or outdoor environment by any chemical, physical or biological agent that modifies the natural characteristics of the atmosphere. Air pollution may cause diseases such as ischemic heart disease, stroke, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, lung cancer, and acute lower respiratory infections.
What is the Pathology of Air Pollution?
The pathology of air pollution is:
-Etiology: The cause of air pollution is pulmonary issues, soot, and carbon monoxide.
-Genes involved: None.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to air pollution is the particulate matter that has been identified as the major bioactive constituent in polluted air. It causes a systemic inflammatory and oxidative stress response
-Morphology: The morphology associated with air pollution shows a complex mixture of thousands of pollutants. This mixture may include solid and liquid particles suspended in the air (particulate matter), and various gases such as ozone, nitrogen oxides, volatile organic compounds, and carbon monoxide.
-Histology: The histology associated with air pollution shows anthracosis in the pulmonary tissue.
How does Air Pollution Present?
Patients with air pollution typically affect males and females both present at the age range of 10-70 years. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with air pollution include tiredness, headache or dizziness, coughing and sneezing, wheezing or difficulty breathing, more mucous in the nose or throat, and dry or irritated eyes, nose, throat, and skin.
How is Air Pollution Diagnosed?
Air pollution is diagnosed by exposure to high concentrations of known pollutants in the air at work and at home or about lung disorders such as asthma, COPD, etc.
How is Air Pollution Treated?
Air pollution is treated and reduced by recycling and reusing, use of public transport, avoiding usage of crackers, use of public transport, etc.
What is the Prognosis of Air Pollution?
The prognosis of air pollution is good if treated early, however, the long-term effects of air pollution may cause permanent health effects such as accelerated lung damage.