Alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma is a subtype of the rhabdomyosarcoma soft tissue cancer family whose lineage is from mesenchymal cells, and which is related to skeletal muscle cells.
What is the Pathology of Alveolar Rhabdomyosarcoma?
The pathology of alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma is:
-Etiology: The cause of alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma is usually sporadic with no genetic predisposition.
-Genes involved: PAX3-FOXO1, PAX7-FOXO1.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma include several genetic recombination events acting together cause the fusion protein, which leads to dysregulation of transcription and acts as an oncogene.
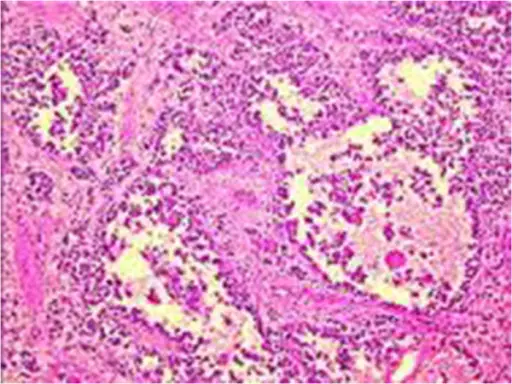
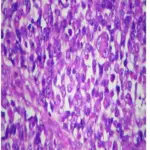
-Histology: The histology associated with alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma shows larger, uniformly round to polygonal cells, variable number of rhabdomyoblasts, multinucleated tumor giant cells with wreath-like nuclei, and mitoses.
How does Alveolar Rhabdomyosarcoma Present?
Patients with alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma typically affect both males and females present at the age range of older children to young adults. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma show a soft mass of tissue that is painless, but the tumor can be detected if it starts to put pressure on other structures in the primary site.
How is Alveolar Rhabdomyosarcoma Diagnosed?
Alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma is diagnosed by immunostaining.
How is Alveolar Rhabdomyosarcoma Treated?
Alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma is treated with standard surgery, radiation therapy, and intensive chemotherapy.
What is the Prognosis of Alveolar Rhabdomyosarcoma?
The prognosis of alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma is poor with a 4-year survival rate.