Ameloblastic fibroma is a rare odontogenic tumor comprising neoplastic epithelial and mesenchymal tissues.
What is the Pathology of Ameloblastic Fibroma?
The pathology of ameloblastic fibroma is:
-Etiology: The cause of ameloblastic fibroma is unknown.
-Genes involved: None.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to ameloblastic fibroma is unclear.
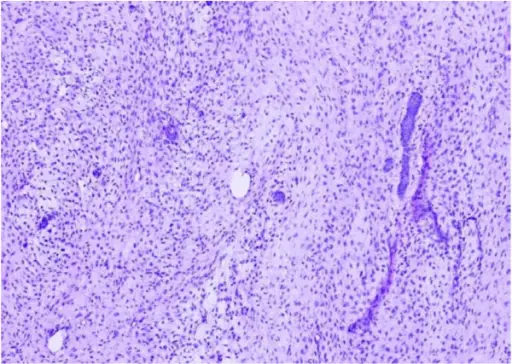
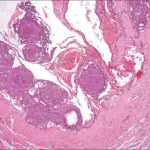
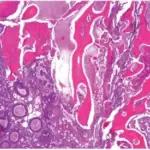
-Histology: The histology associated with ameloblastic fibroma shows small islands and cords of markedly attenuated ameloblastic epithelium two cells thick within dense collagenous stroma that is often immature.
How does Ameloblastic Fibroma Present?
Patients with ameloblastic fibroma typically affect females present in the age range of 40-60 years. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with ameloblastic fibroma include; Small tumors are asymptomatic, while larger ones produce significant swelling of the jaws
How is Ameloblastic Fibroma Diagnosed?
Ameloblastic fibroma is diagnosed by radiography and histology.
How is Ameloblastic Fibroma Treated?
Ameloblastic fibroma is treated by enucleation and curettage. However, extensive and aggressive lesions may require radical treatment such as excision.
What is the Prognosis of Ameloblastic Fibroma?
The prognosis of ameloblastic fibroma is good.