Amphetamine Injury is the injury caused by the drug amphetamine. Amphetamine is a CNS stimulant, use to treat attention deficit hyperactivity disorder.
What is the Pathology of Amphetamine Injury?
The pathology of amphetamine injury is:
-Etiology: The cause of amphetamine injury is smoking and drug overdose.
-Genes involved: None.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to amphetamine injury shows inhibition of specific transporters responsible for the reuptake of biogenic amines from the synaptic nerve ending and presynaptic vesicles.
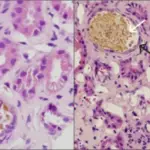
-Morphology: The morphology associated with amphetamine injury shows 5 HT axons.
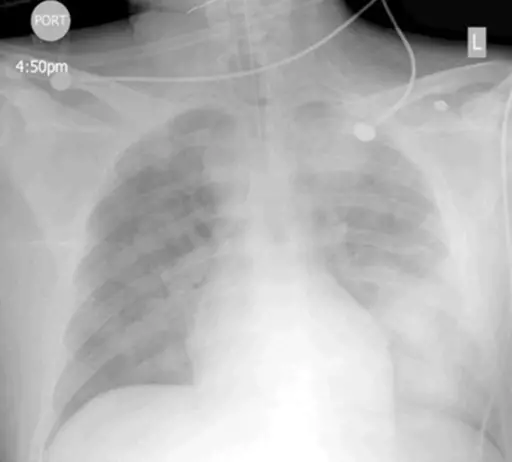
-Histology: The histology associated with amphetamine injury shows alveolar rupture and terminal asphyxia.
How does Amphetamine Injury Present?
Patients with amphetamine injury typically affect males and females both present at the age range of 18-55. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with amphetamine injury include agitation, psychosis, seizures, hypertension, tachycardia, hyperthermia, stroke, and potentially life-threatening cardiac dysrhythmias.
How is Amphetamine Injury Diagnosed?
Amphetamine injury is diagnosed using blood tests, CT scans.
How is Amphetamine Injury Treated?
Amphetamine injury is treated with gastric decontaminants, sedatives, muscle relaxants, and other drugs.
What is the Prognosis of Amphetamine Injury?
The prognosis of amphetamine injury is fair as the symptoms can be reversed.