Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis is a progressive nervous system disease that affects nerve cells in the brain and spinal cord, causing loss of muscle control. ALS is also known as Lou Gehrig’s disease, after the baseball player who was diagnosed with it.
What is the Pathology of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis?
Etiology: The cause of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis is genetic in 5% to 10% of the people. For the rest, the cause isn’t known.
Genes involved: Unknwn.
Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis is upper motor neuron and lower motor neuron signs.
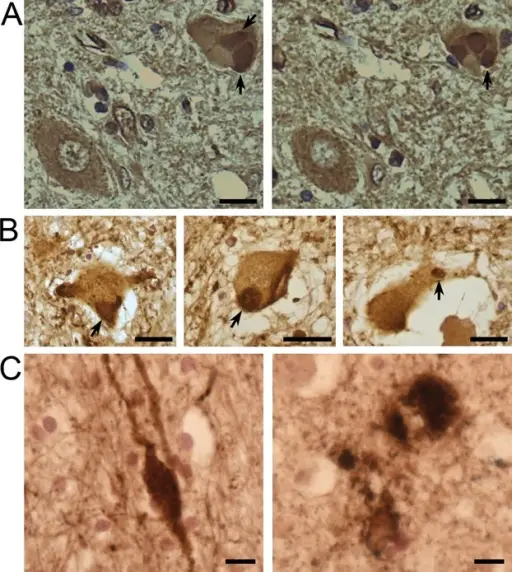
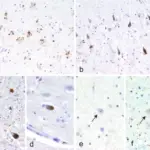
Histology: The histology associated with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis shows ubiquinated inclusions in lower motor neurons and axonal swellings that are thought to contain disarrayed neurofilaments.
How does Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Present?
Patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis are usually males before the age of 65 years old. After 70 years, there is no sex difference. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis include difficulty walking, weakness, slurred speech, cramps, and clumsiness.
How is Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Diagnosed?
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis is diagnosed by history, physical examination, and electromyography (EMG).
How is Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Treated?
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis is symptomatically managed. The medication Riluzole may be helpful.
What is the Prognosis of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis?
The prognosis of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis is poor and the disease is fatal.