The adenomatoid tumor is a well-recognized slow-growing benign tumor derived from a complex system of the dental lamina or its remnants.
What is the Pathology of an Adenomatoid Tumor?
The pathology of adenomatoid tumor is:
-Etiology: The cause of the adenomatoid tumor is unknown.
-Genes involved: None.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to the adenomatoid tumor is unknown.
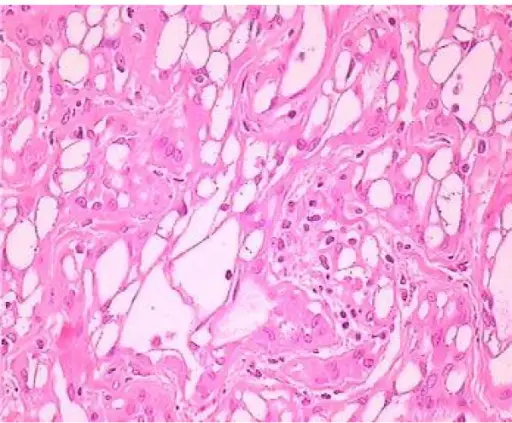
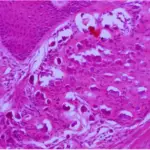
-Histology: The histology associated with adenomatoid tumors shows tubules, cords, or small nests composed of or lined with cuboidal cells.
How does Adenomatoid Tumor Present?
Patients with Adenomatoid tumors typically affect males and females present in the age range of 18-80 years. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with adenomatoid tumors include painless, firm masses of <2 cm diameter.
How is Adenomatoid Tumor Diagnosed?
An adenomatoid tumor is diagnosed primarily through biopsy.
How is Adenomatoid Tumor Treated?
The adenomatoid tumor is treated by surgical excision.
What is the Prognosis of an Adenomatoid Tumor?
The prognosis of an adenomatoid tumor is fair.