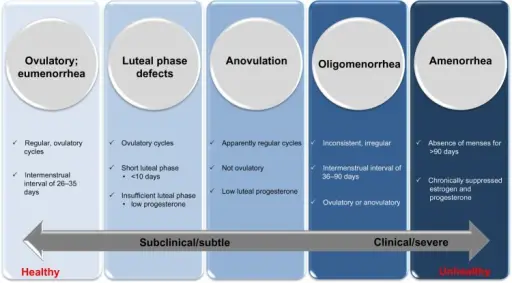
Anovulatory cycle is a menstrual cycle in which ovulation, or the release of an egg from the ovaries, does not occur.
What is the Pathology of Anovulatory Cycle?
The pathology of anovulatory cycle is:
-Etiology: The cause of anovulatory cycle is hormonal imbalances that can be the result of using hormonal birth control, being underweight or overweight, exercising excessively, or experiencing significant stress.
-Genes involved: GNRH1 gene.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to anovulatory cycle are: the imbalance in hormones released from hypothalamo-pituitary axis which controls egg release via the ovarian cycle, or other endocrine abnormalities, to the ovary itself.
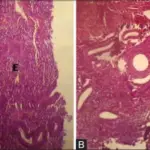
-Morphology: The morphology associated with anovulatory cycle shows disordered and unstable uterine lining.
-Histology: The histology associated with anovulatory cycle shows characteristic endometrial tissue.
How does Anovulatory Cycle Present?
Patients with anovulatory cycle typically females who are close to menopause or 40 to 50 years old. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with anovulatory cycle include no periods, no cervical mucus, excessive bleeding in periods, irregular basal body temperature, infertility, inability to get pregnant.
How is Anovulatory Cycle Diagnosed?
Anovulatory cycle is diagnosed by testing blood progesterone levels, thyroid and prolactin levels, ultrasound, testing for certain antibodies, uterine lining testing.
How is Anovulatory Cycle Treated?
Anovulatory cycle is treated by lifestyle changes, nutritional improvements, weight loss, clomiphene citrate to trigger release of egg.
What is the Prognosis of Anovulatory Cycle?
The prognosis of anovulatory cycle is good. Because many different factors influence a woman’s hormones and menstrual cycle, there is no one solution for treating anovulation.