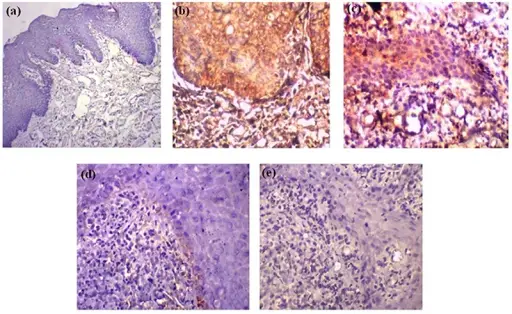
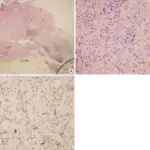
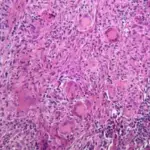
Irritation fibromas are fibrous nodules of the oral cavity, often considered to be reactive hyperplasia secondary to trauma or other local sources of irritation.
What is the Pathology of Irritation Fibroma?
The pathology of irritation fibroma is:
-Etiology: The cause of irritation fibroma is usually due to chronic irritation such as Cheek or lip biting. Rubbing from a rough tooth. Dentures or other dental prostheses.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to irritation occurs in response to local irritation or trauma and is characterized by the proliferation of collagenous connective tissue and blood vessels.
How does Irritation Fibroma Present?
Patients with irritation fibroma typically affect females present at the age range of 40-60 years. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with irritation fibromas include that irritation fibromas usually manifest an exophytic, firm, and asymptomatic nodule with a pink or flesh-colored and smooth surface. The nodule often has a well-defined boundary. It is slow-growing and rarely exceeds 1.5 cm in diameter.
How is Irritation Fibroma Diagnosed?
Irritation fibroma is diagnosed clinically through biopsy.
How is Irritation Fibroma Treated?
Irritation fibroma is treated by surgical excision.
What is the Prognosis of Irritation Fibroma?
The prognosis of irritation fibroma is usually very good.