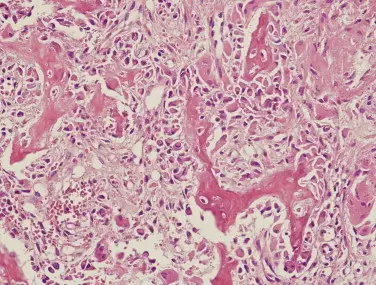
Osteoblastoma is a rare benign bone-forming neoplasm which produces woven bone spicules, which are bordered by prominent osteoblasts.
What is the Pathology of Osteoblastoma?
The pathology of osteoblastoma is:
-Etiology: The cause of osteoblastoma is unknown.
-Genes involved: MDM2, TP53, and PNCA.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to osteoblastoma expresses Runx2 and osterix, transcription factors involved in osteoblastic differentiation.
-Histology: The histology associated with osteoblastoma shows anastomosing woven bone trabeculae, lined by a single but prominent layer of osteoblasts, and intervening hypervascular, hypocellular intertrabecular spaces.
How does Osteoblastoma Present?
Patients with osteoblastoma typically affect males more than females in 20-30 years of age. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with osteoblastoma include pain of several months in duration.
How is Osteoblastoma Diagnosed?
Osteoblastoma is diagnosed by X-ray, MRI, and CT scan.
How is Osteoblastoma Treated?
Osteoblastoma is treated by surgical excision.
What is the Prognosis of Osteoblastoma?
The prognosis of osteoblastoma is excellent, with most patients cured following the initial surgical treatment.