Anaplastic carcinoma is the most aggressive malignancy of the thyroid gland.
What is the Pathology of Anaplastic Carcinoma?
The pathology of anaplastic carcinoma is:
-Etiology: The cause of anaplastic carcinoma is unclear but could be associated with iodine deficiency and radiation.
-Genes involved: None.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to anaplastic carcinoma involves the anaplastic transformation of differentiated thyroid carcinoma.
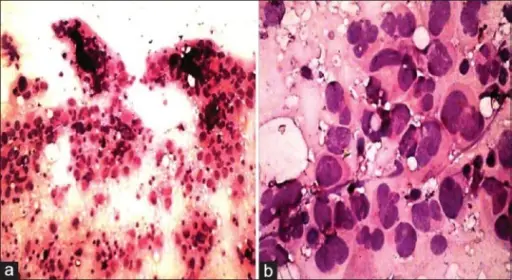
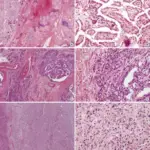
-Histology: The histology associated with anaplastic carcinoma shows widely invasive growth, extensive tumor necrosis, marked nuclear pleomorphism, and high mitotic activity.
How does Anaplastic Carcinoma Present?
Patients with anaplastic carcinoma typically occur in females present at the age range of 60 -70 years. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with anaplastic carcinoma include multinodular goiter, rapidly enlarging, painful, firm, ill-defined, lower anterior neck mass, hoarseness, dyspnea, and dysphagia.
How is Anaplastic Carcinoma Diagnosed?
Anaplastic carcinoma is diagnosed using neck imaging studies such as ultrasound, CT scan, or MRI.
How is Anaplastic Carcinoma Treated?
Anaplastic carcinoma is treated radiation therapy or chemotherapy.
What is the Prognosis of Anaplastic Carcinoma?
The prognosis of anaplastic carcinoma is poor as hardly half of the people survive after they are diagnosed with anaplastic carcinoma.