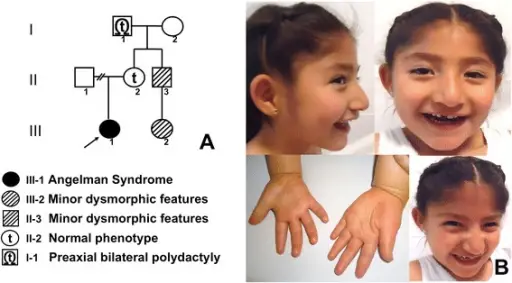
Angelman syndrome is a complex genetic disorder that primarily affects the nervous system.
What is the Pathology of Angelman Syndrome?
The pathology of Angelman syndrome is:
-Etiology: The cause of Angelman syndrome is deficiency of the E3 ubiquitin protein ligase (UBE3A) gene expression.
-Genes involved: UBE3A gene on maternal copy of chromosome 15.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to Angelman syndrome is a lack of expression of a gene UBE3A during development. Paternally derived UBE3A is silenced. Disease occurs when the maternal allele is deleted or mutated.
How does Angelman Syndrome Present?
Patients with Angelman syndrome may be male or female, and are typically younger. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with Angelman syndrome include seizures, ataxia, severe intellectual disability, inappropriate laughter.
How is Angelman Syndrome Diagnosed?
Angelman syndrome is diagnosed based on a history of delayed motor milestones and then later a delay in general development, unusual movements, frequent laughing, hand flapping, and a wide-based gait. Genetic testing for deletion or inactivity on chromosome 15 by array comparative genomic hybridization (aCGH) or by BACs-on-Beads technology may be helpful.
How is Angelman Syndrome Treated?
Angelman syndrome is treated with supportive care.