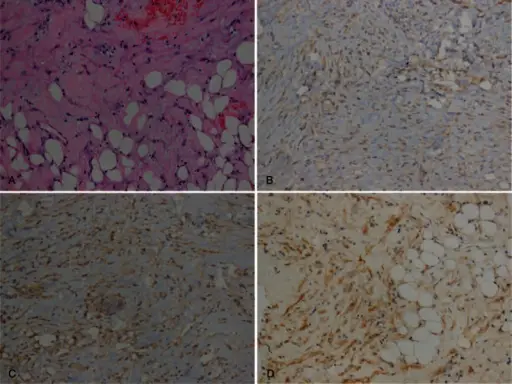
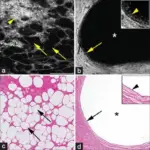
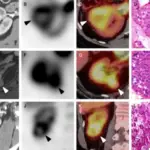
Angiomyolipoma is a benign renal neoplasm consisting of fat, vascular components, and smooth muscle.
What is the Pathology of Angiomyolipoma?
The pathology of angiomyolipoma is:
-Etiology: The cause of tuberous sclerosis is unknown.
-Genes involved: TSC2.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to angiomyolipoma unclear
-Morphology: Not applicable.
-Histology: Vascular, muscle, and fat cells in the kidney.
How does Angiomyolipoma Present?
Patients with angiomyolipoma typically have higher preference in females present at the age range of 40 to 60 years. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with angiomyolipoma include palpable abdominal mass, flank pain, hematuria, shock, and acute abdomen.
How is Angiomyolipoma Diagnosed?
Angiomyolipoma is diagnosed by clinical presentation. Imaging studies such as ultrasound shows a hyperechoic lesion, CT scan, and MRI, and percutaneous biopsy.
How is Angiomyolipoma Treated?
Angiomyolipoma is treated by selective renal artery embolization, complete nephrectomy, nephron-sparing surgery, cryo- and radiofrequency ablation, and management with mTOR inhibitors.
What is the Prognosis of Angiomyolipoma?
The prognosis of angiomyolipoma is good, with prompt management.