Antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies vasculitis is an autoimmune disease of the small blood vessels that are directed to the damage of certain proteins in the blood vessels.
What is the Pathology of Antineutrophilic Cytoplasmic Antibodies Vasculitis?
The pathology of antineutrophilic cytoplasmic antibodies vasculitis is:
-Etiology: The cause of anti-neutrophilic cytoplasmic antibodies vasculitis is the presence of the antibodies.
-Genes involved: HLA genes.
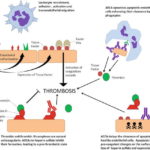
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to antineutrophilic cytoplasmic antibodies vasculitis is not known but two mechanisms are involved. theory of molecular mimicry and the theory of defective apoptosis.
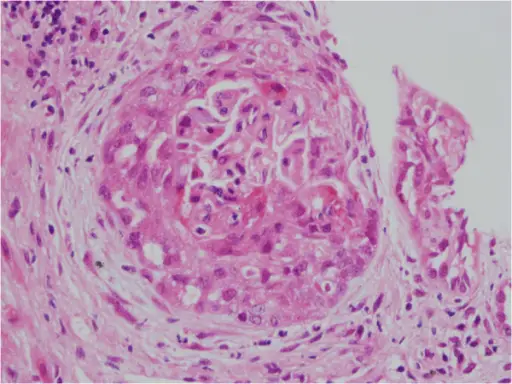
-Morphology: The morphology associated with anti-neutrophilic cytoplasmic antibodies shows pauci-immune necrotizing crescentic glomerulonephritis.
-Histology: Vasculature with proteinaceous deposition.
How does Antineutrophilic Cytoplasmic Antibodies Present?
Patients with antineutrophilic cytoplasmic antibodies typically are middle aged adults. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with antineutrophilic cytoplasmic antibodies include proteinuria, hematuria, high blood pressure, fatigue, respiratory failure, tracheal inflammation.
How are Antineutrophilic Cytoplasmic Antibodies Diagnosed?
Anti-neutrophilic cytoplasmic antibodies are diagnosed by microscopy, urinalysis, kidney function tests, creatinine levels, and blood tests.
How is Antineutrophilic Cytoplasmic Antibodies Treated?
Anti-neutrophilic cytoplasmic antibodies are treated by glucocorticoids, cyclophosphamides, plasma exchange therapy.
What is the Prognosis of Antineutrophilic Cytoplasmic Antibodies?
The prognosis of antineutrophilic cytoplasmic antibodies is poor since it has a high mortality rate of 90%