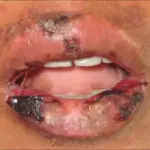
Antiphospholipid antibody syndrome is an acquired autoimmune disease that manifest as recurrent thrombosis or fetal loss in pregnant women. It is a condition that alters the regulation of blood coagulation.
What is Antiphospholipid Antibody Syndrome?
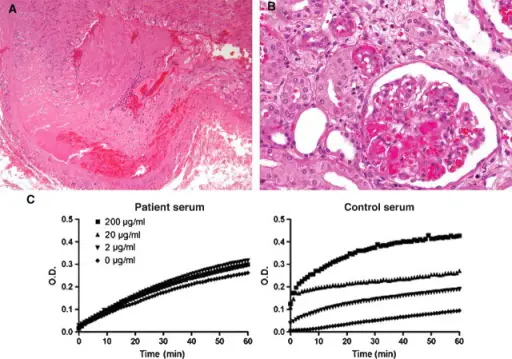
(A) Explant nephrectomy performed on Day 5. There is extravasation of red cells and fibrin in the muscular wall and thrombosis of the renal artery (H&E ×100). (B) Explant nephrectomy. Glomerular capillary thrombi and thickening and endothelial swelling in adjacent arteriole (H&E ×200). (C) Kinetics of kallikrein activation by negatively charged molecules. Patient serum (30 μl) or control human serum (30 μl) was incubated with 20 μl of oversulfated glycosaminoglycans (OS-GAG) at a final concentration of 0, 2, 20 and 200 μg/ml at 37°C for 5 min. Kallikrein amidolytic activity was assessed by addition of 150 μl of 50 mM N-Benzoyl-Pro-Phe-Arg-p-nitroanilide hydrochloride chromogenic substrate. O.D. readings were taken every minute for 60 min. The auto-activated kallikrein activities (without OS-GAG induction) in patient serum suggest the presence of a negatively charged contact system inducer in the patient's blood.Acute renal allograft thrombosis in 'seronegative' antiphospholipid syndrome.
Akilesh S, Jendrisak M, Zhang L, Lewis JS, Liapis H - NDT plus (2009). Not Altered. CC.