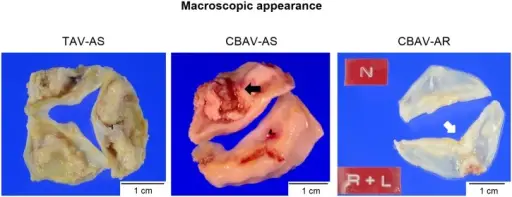
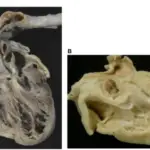
Aortic stenosis is the narrowing of the aortic valve, reducing or blocking blood flow from the heart to the body.
What is the Pathology of Aortic Stenosis?
Aortic stenosis pathology includes narrowing of the aortic valve in the valvular, subvalvular, or supra-valvular area that may be due to a fibrous ring or membrane.
How Does Aortic Stenosis Present?
Aortic stenosis is more common in males and asymptomatic in children with mild to moderate aortic stenosis. Severe aortic stenosis may present as chest pain with exertion, low exercise tolerance, and syncope.
How is Aortic Stenosis Diagnosed?
Aortic stenosis diagnosis includes electrocardiogram, chest x-ray, serum electrolyte levels, cardiac biomarkers, and CBC. 2D echo confirms diagnosis.
How is Aortic Stenosis Treated?
Aortic stenosis treatment includes IV prostaglandin to maintain an open ductus arteriosus for an alternative blood flow. Mild to moderate aortic stenosis only requires supportive management; severe cases are treated with balloon valvuloplasty.
What is the Prognosis of Aortic Stenosis?
Aortic stenosis prognosis is excellent for the asymptomatic with less than 1% mortality per year; however, patients with severe aortic stenosis have a poor prognosis with 40% mortality in all patients.