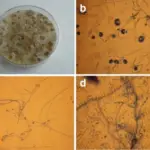
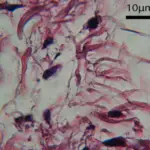
Aspergillosis fungal Infection is an infection caused by a type of mold fungus. The illnesses resulting from aspergillosis infection usually affect the respiratory system.
What is the Pathology of Aspergillosis Fungal Infection?
The pathology of aspergillosis fungal infection is:
-Etiology: The cause of aspergillosis fungal infection is Aspergillus, a common mold.
-Genes involved: Not applicable.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to aspergillosis fungal infection includes the inhalation of airborne conidia and deposition in the bronchioles or alveolar spaces
-Morphology: The morphology associated with aspergillosis fungal infection shows filamentous fungi, which means that they tend to form filaments. A. niger consists of smooth and colorless conidiophores and spores.
-Histology: The histology associated with aspergillosis fungal infection shows dense acute infiltrate in the dermis and deep soft tissue associated with necrosis and scarring.
How does Aspergillosis Fungal Infection Present?
Patients with aspergillosis fungal infection typically are all genders of all ages. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with aspergillosis fungal infection include skin lesions, shortness of breath, chest pain, joint pain, headaches, fever, and chills.
How is Aspergillosis Fungal Infection Diagnosed?
Aspergillosis fungal infection is diagnosed by biopsy, x-rays, antigen skin tests, tissue culture or blood tests.
How is Aspergillosis Fungal Infection Treated?
Aspergillosis fungal infection is treated by voriconazole, and Amphotericin B.
What is the Prognosis of Aspergillosis Fungal Infection?
The prognosis of aspergillosis fungal infection is poor if pulmonary aspergillosis occurs. Invasive aspergillosis is associated with significant mortality, with a rate of 30-95%.