Aspirin Injury is the injury due to aspirin intake.
What is the Pathology of Aspirin Injury?
The pathology of aspirin injury is:
-Etiology: The cause of aspirin injury is drug overdose
-Genes involved: None.
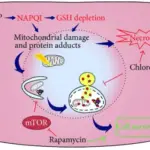
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to aspirin injury includes disrupting the hydrophobicity of mucus HCO3− the protective layer of the gastric mucosa.
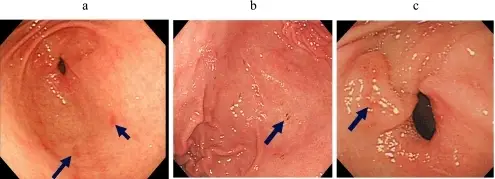
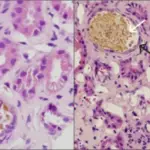
-Morphology: The morphology associated with aspirin injury shows signs of cytolysis in situ or as desquamation.
-Histology: The histology associated with aspirin injury shows gastric lesion consisting of loss of mucus and an alteration in nuclear appearance.
How does Aspirin Injury Present?
Patients with aspirin injury typically affect males and females present at the age range of 25-45. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with aspirin injury include ringing in the ears, nausea, vomiting, drowsiness, confusion, and rapid breathing.
How is Aspirin Injury Diagnosed?
Aspirin injury is diagnosed using simple blood tests.
How is Aspirin Injury Treated?
Aspirin injury is treated with anti-inflammatory and typical antibiotics.
What is the Prognosis of Aspirin Injury?
The prognosis of aspirin injury is fair with complete recovery.