Asthma is immunologic bronchoconstriction, inflammation, and mucus production due to increased airway sensitivity.
Types of asthma include:
- Atopic Asthma
- Drug-Induced Asthma
- Exercise-Induced Asthma
- Non-Atopic Asthma
- Occupational Asthma
What is the Pathology of Asthma?
The pathology of asthma is:
-Etiology: The cause of asthma is, atopy, environmental factor including sensitizing chemicals, air pollution by allergens, or indoor allergens.
-Genes involved: ORMDL3 gene.
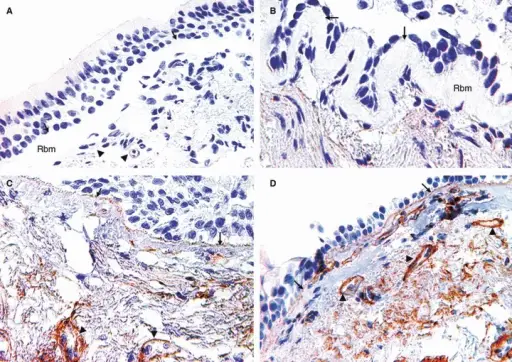
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to asthma areas follows. Airway inflammation. Walls are infiltrated by inflammatory cells, eosinophils, neutrophils, plasma, cells, and lymphocytes which causes hyperemia, mucosal and submucosal edema. Intermittent airflow obstruction due to edema and finally bronchial hyperresponsiveness.
-Histology: The histology associated with asthma shows permeation of the inflammatory cells, airway lumina taping, mucus masses, and bronchial/bronchiolar epithelial stripping.
How does Asthma Present?
Patients with asthma typically a male-to-female ratio of 2:1 in children and 1:1 in adults, present at age range of 18 years. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with asthma include chest tightness, wheezing, shortness of, breath and cough frequently worse at night.
How is Asthma Diagnosed?
Asthma is diagnosed through medical and physical examination, laboratory studies which include spirometry assessments, peak flow monitoring, sputum and blood eosinophils.
How is Asthma Treated?
Asthma is treated through environmental control for allergens and pharmacologic treatment.
What is the Prognosis of Asthma?
The prognosis of asthma is good with proper treatment and management.