Ataxia telangiectasia is a very rare inherited disorder that affects the immune system, and nervous system.
What is the Pathology of Ataxia-Telangiectasia?
The pathology of ataxia-telangiectasia is:
-Etiology: The cause of ataxia-telangiectasia is mutations in the ATM.
-Genes involved: Ataxia telangiectasia mutated (ATM).
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to ataxia-telangiectasia are as a result of ATM gene mutation, which speciously controls the cell cycle and plays a key role in the guard of the genome.
-Morphology: The morphology associated with ataxia-telangiectasia shows progeric skin variations.
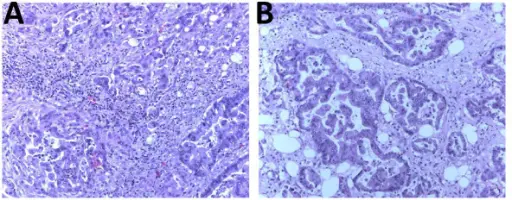
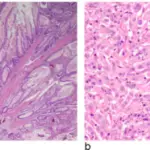
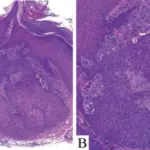
-Histology: The histology associated with ataxia-telangiectasia shows different granulomatous patterns.
How does Ataxia Telangiectasia Present?
Patients with ataxia-telangiectasia typically are children below the age of 5 years old and equally among males and females. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with ataxia-telangiectasia include difficulty in movement coordination, inability to balance self, muscle twitching, slurred speech, clusters of the blood vessel are seen on the eyes.
How is Ataxia-Telangiectasia Diagnosed?
The ataxia-telangiectasia is diagnosed mostly by physical examination, history taking, a blood sample to identify the level of alpha-fetoprotein, genetic testing, and MRI.
How is Ataxia-Telangiectasia Treated?
The ataxia-telangiectasia is treated by the use of antibiotics, injection with immunoglobulins to lower chances of infection, use of beta-adrenergic blockers, regular screening to detect cancer.
What is the Prognosis of Ataxia-Telangiectasia?
The prognosis of ataxia-telangiectasia is poor if there is the involvement of the pulmonary system since most patients die during adolescence.