Atelectasis is the fractional or total complete collapse of the lung or a specific portion of the lung. Incomplete expansion of the lungs (Neonatal Atelectasis).
What is the Pathology of Atelectasis?
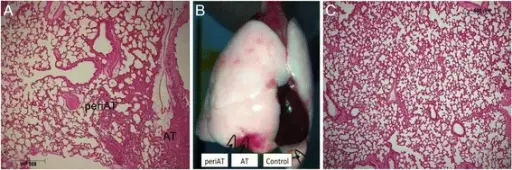
The pathology of atelectasis is: Incomplete expansion of the lungs or partial/total Collapse collapse of the lungs leading to impaired gaseous exchange.
-Etiology: The cause of atelectasis is, impaired surfactant production, bronchial impediment by foreign bodies, growths, plugs of sputum, or endobronchial tumors.
-Genes involved: surfactant protein A (SPA1, SPA2).
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to atelectasis is collapsed alveoli.
-Histology: The histology associated with atelectasis shows collapsed alveoli.
How does Atelectasis Present?
Patients with atelectasis typically have no gender predilection, present at age range of 60 years. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with atelectasis include chest pain, abrupt dyspnea, and cyanosis, tachycardia hypotension, shock and fever.
How is Atelectasis Diagnosed?
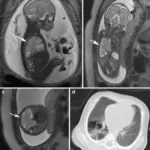
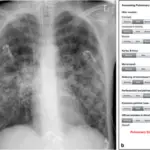
Atelectasis is diagnosed through laboratory studies, ABGs determine hypoxemia. Imaging studies, CT scans, and chest radiology check for lobar collapse. Bronchoscopy assesses bronchial obstruction.
How is Atelectasis Treated?
Atelectasis is treated through medical care, oxygen therapy, mechanical and intubation support, CPAP, a broad-spectrum antibiotic, treatment of underlying causes, chest physiotherapy, and nebulization.
What is the Prognosis of Atelectasis?
The prognosis of atelectasis is fair.