Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease is a genetic disorder also called adult polycystic kidney disease, characterized by renal failure following multiple expanding cysts of both kidneys that eventually destroy the renal parenchyma.
What is the Pathology of Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease?
The pathology of autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease is:
-Etiology: The cause of autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease is genetic.
-Genes involved: PKD1 and PKD2 gene.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease follows a range of dissimilar mutations in PKD1 and PKD2 leading to numerous cellular fluctuations allied with cyst advancement.
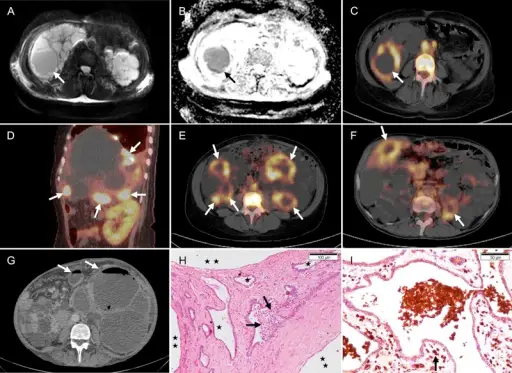
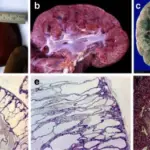
-Morphology: The morphology associated with autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease shows bilaterally enlargement of kidneys, composition of cyst masses.
-Histology: The histology associated with autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease shows operational nephrons dispersed between the cysts which are filled with turbid, red to brown fluid.
How does Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease Present?
Patients with autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease typically high in males present at the age range of 50 to 70 years. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease include asymptomatic, abdominal masses, proteinuria, polyuria, and hypertension.
How is Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease Diagnosed?
Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease is diagnosed through imaging studies such as ultrasonography, CT scan, MRI/MRA. Laboratory studies such as genetic study, serum chemistry profile, urine culture, uric acid determination, intact parathyroid hormone assay.
How is Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease Treated?
Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease is treated through pharmacological therapy for symptomatic support, vasopressin V2-receptor antagonist (tolvaptan). Surgical drainage of cystic fluid fill.
What is the Prognosis of Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease?
The prognosis of autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease is fair.