B-cell prolymphocytic leukemia is a very rare and typically aggressive malignancy (cancer) characterized by the out of control growth of B-cells (B-lymphocytes).
What is the Pathology of B-cell Prolymphocytic Leukemia?
The pathology of b-cell prolymphocytic leukemia is:
-Etiology: The cause of b-cell prolymphocytic leukemia is largely unknown.
-Genes involved: TP53 gene, MYC gene.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to b-cell prolymphocytic leukemia most of the time occurs as a transformation or evolution of a more slow-growing B-cell cancer, such as chronic lymphocytic leukemia.
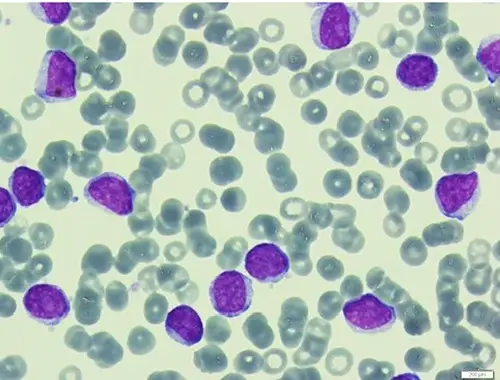
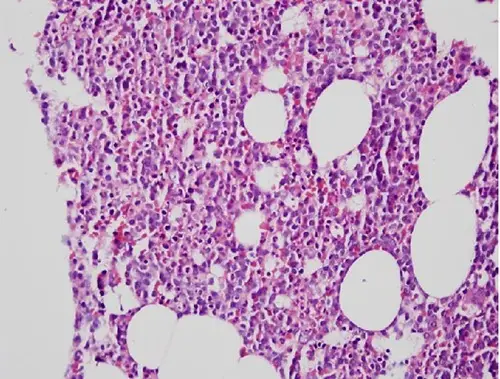
-Histology: The histology associated with b-cell prolymphocytic leukemia shows large lymphoid cells (prolymphocytes) accounting for at least 55% of total circulating cells in the peripheral blood.
How does B-Cell Prolymphocytic Leukemia Present?
Patients with b-cell prolymphocytic leukemia typically are >60 years with a median age at diagnosis of 65-69 years. It is slightly more common in men than women. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with b-cell prolymphocytic leukemia include high lymphocyte count, splenomegaly, B-symptoms (fevers, night sweats, weight loss), anemia and thrombocytopenia.
How is B-Cell Prolymphocytic Leukemia Diagnosed?
B-cell prolymphocytic leukemia is diagnosed by complete blood count, peripheral blood smear, bone marrow aspirate/biopsy, immunophenotyping by flow cytometry, cytogenetics either by karyotyping or FISH and molecular testing.
How is B-Cell Prolymphocytic Leukemia Treated?
B-cell prolymphocytic leukemia is treated by chemo-immunotherapy combinations used to treat chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Common regimens include fludarabine, cyclophosphamide, and rituximab or bendamustine and rituximab. In patients who achieve a remission following initial drug therapy, hematopoietic stem cell transplantation is a treatment option that may offer a potential cure.
What is the Prognosis of B-Cell Prolymphocytic Leukemia?
The prognosis of b-cell prolymphocytic leukemia is poor (median survival of 3 years). The presence of high-risk genetic mutations 17P/TP53 deletion translates into poor prognosis.