Basal cell adenoma is an uncommon type of monomorphous adenoma.
What is the Pathology of Basal Cell Adenoma?
The pathology of basal cell adenoma is:
-Etiology: The cause of basal cell adenoma is unknown.
-Genes involved: CTNNB1 mutations, CYLD1 mutations
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to basal cell adenoma is unknown.
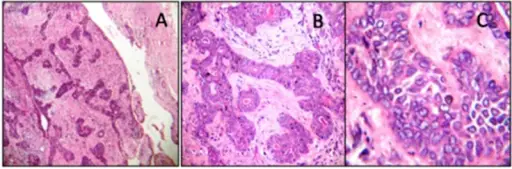
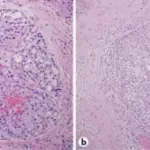
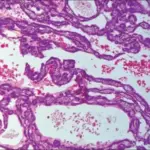
-Histology: The histology associated with basal cell adenoma shows 2 types of cells which include basaloid cells and luminal cells. Fibrocellular stroma may also be present.
How does Basal Cell Adenoma Present?
Patients with basal cell adenoma typically are women present at an age range of between their fifth and seventh decades of life. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with basal cell adenoma include a firm and mobile, slow growing, painless mass.
How is Basal Cell Adenoma Diagnosed?
Basal cell adenoma is diagnosed by imaging, fine needle aspiration, and biopsy.
How is Basal Cell Adenoma Treated?
Basal cell adenoma is treated by a surgical excision.
What is the Prognosis of Basal Cell Adenoma?
The prognosis of basal cell adenoma is good.